Technology/
High Efficiency Video Coding: HEVC
Significantly better compression of next-generation video using HEVC. Learn more about our unique implementation of HEVC encoder and decoder.
Video Codec Evolution
Video compression technology has played a paramount role in the success of media applications in the last decades. In the early 90s MPEG-1 and H.261 codecs made feasible the transmission of low-resolution video using reduced bandwidth networks. Since the mid-90s MPEG-2 has been used extensively in DVD and Digital TV broadcast. H.264/AVC, standardized in 2003, has become the most widely used video codec for HD video distribution in broadcast, VoD, and Blu-ray.

To meet the demands of new applications requiring even higher quality, such as Ultra-HD TV with 4K and 8K, the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standard (also known as H.265) was developed and ratified in 2013. HEVC/H.265 currently represents the state-of-the-art in UHD compression for real-time workflows. It is capable of reducing the bitrate by 50% for the same quality compared to H.264/AVC. Despite some issues related to IP licensing, the HEVC standard has been widely deployed in the media industry, driving especially the shift to UHD video.
AV1 has been developed by the Alliance Open Media (AOM) with the main objective of being royalty-free for Internet streaming applications. The AV1 codec has been promoted as an alternative to HEVC with its claimed royalty-free model and potentially higher compression efficiency. Based on recent studies, AV1 has the potential to achieve up to 21% average bitrate savings for the same quality compared to the HEVC reference software at the cost of 5x higher encoding complexity.
The new-generation coding standard called Versatile Video Coding (VVC)/H.266 was completed in July 2020. VVC produces a 50% bitrate reduction over HEVC for the same quality at the expense of 8x higher encoding complexity.
The HEVC Standard
The HEVC/H.265 standard has been developed by the ITU-T video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Moving Pictures Experts Group (MPEG) standardization organizations, which have joined together in a partnership known as the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC).
HEVC provides many tools which together result in significant compression benefits compared to H.264/AVC. A tool is basically a video coding technique that allows the encoder to obtain video compression gains.
HEVC represents the state-of-the-art in 4K and 8K video compression for real-time workflows and has been widely deployed in the broadcast, VoD and other industries.
Examples of coding tools in HEVC include:
- Larger block size extended to 64×64 instead of the 16×16 size of previous standard
- Ability to subdivide blocks recursively into smaller blocks with a maximum depth as a parameter
- Many more intra prediction modes: 35 modes instead of 10 in H.264
- Advanced Motion Vector (MV) prediction technique
- Advanced in-loop filters including deblocking filter and Sample Adaptive Offset (SAO)
- Enhanced Context-based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC)

The HEVC standard includes additional support for HDR and WCG video quality enhancements, as well as support for temporal scalability for frame rate adaptation to heterogeneous devices (TVs, PCs, tablets, smartphones), and hierarchical Group of Pictures (GOPs) that result in higher compression gains compared to traditional coding structures.
Additionally, in order to benefit from the now widespread parallel multicore architectures, tools specially devoted for parallel processing been designed, namely: Wavefront Parallel Processing (WPP) and Tiles. Both of these tools allow subdivision of each picture into multiple partitions that can be processed in parallel.
The HEVC/H.265 standard has been enhanced with several key extensions:
- RExt (HEVC version 2, 2014): which extends the range of color formats and bit depth to allow for very high-quality coding; including support for 4:2:2, 4:4:4, and RGB formats and bit-depths up to 12-bit
- Scalability (HEVC version 2, 2014): which enables from a complete bitstream the extraction of one or a subset of sub-streams with lower spatio-temporal resolutions or reduced quality versions of the original video sequence
- Multiview (HEVC version 2, 2014): which supports coding of multiple views of the scene
- 3D video (HEVC version 3, 2015): which makes possible the efficient compression of multiple views required for glasses-free 3D
- Screen Content Coding – SCC (HEVC version 4, 2016): which adds special tools to improve the compression of rendered video, text, and animation
As a result, HEVC allows for not only enhanced features to the traditional video applications, such as TV broadcast, VoD, and storage, but also to extend the range of applications to include VR and panoramic video, immersive projections, game streaming, remote desktop, and ultra-low-latency video conferencing.
Coding Tools and Applications for Different Codecs
The table below shows a comparison between HEVC and MPEG-2 and H.264, from different perspectives: coding tools, features, extensions, and applications.
| MPEG-2 | H.264/AVC | HEVC/H.265 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coding tools | Largest block size | 16x16 | 16x16 | 64x64 |
| Smallest prediction unit | 16x16 | 8x8, 4x4 | Inter 8x4, Inter 4x8, Intra 4x4 | |
| Transform unit sizes | 8x8 | 8x8, 4x4 | 32x32 down to 4x4 | |
| Prediction | No Intra, half pel MV precision, maximum 2 reference frames | 10 Intra modes, quarter pel MV precision, up to 16 reference frames | 35 Intra modes, quarter pel MV precision, 8-tap filter, advanced motion vector prediction, up to 16 reference frames | |
| In-loop filters | None | Deblocking | Deblocking improved, SAO | |
| Entropy coding | VLC | CAVLC, CABAC | CABAC enhanced | |
| Features | slices | slices | HDR, WCG, temporal scalability, hierarchical GOPs, slices, WPP, Tiles | |
| Extensions | 4:2:2, 4:4:4, scalability | 4:2:2, 4:4:4, up to 16 bit-depth, scalability, multiview | 4:2:2, 4:4:4, up to 16 bit-depth, scalability, multiview, 3D, SCC | |
| Applications | Standard TV, DVD | HD TV, Blu-ray, Internet video | UHD TV, 4K Blu-ray, Internet video, VR, immersive projections, game streaming, remote desktop, low latency video conferencing |
Spin Digital HEVC Codec Implementation
The HEVC standard specifies the decoding method for valid bitstreams. Different implementations can have different features and performance levels. Bitstreams decoded by different decoders should produce exactly the same video output, but different decoders can have very different performance levels. Different encoders are required to produce valid bitstreams according to the specification, but they can have a very different quality, compression, and performance level.
Spin Digital has developed a high-quality and high-performance software implementation of the HEVC codec.
High-performance Decoder
The Spin Digital HEVC software decoder has been extensively optimized in order to achieve an unparalleled level of performance, including:
- Advanced multithreading for maximum performance and scalability on multicore architectures with tens of processor cores
- Advanced library of SIMD optimized modules for SSE4, AVX2, and AVX-512 instruction sets
- Extensive memory optimizations to reduce memory bandwidth using efficient pixel formats and cache-friendly data structures
Spin Digital’s HEVC software decoder is able to process in real-time very demanding video formats, such as 16Kp60 or 8Kp120, on a single workstation with 48 cores.
High-quality Real-time Encoder
Spin Digital’s software encoder is tailored to live 4K, 8K, and beyond video applications. The encoder delivers similar quality to offline encoders at significantly higher encoding speeds, and higher quality than real-time software and hardware-accelerated encoders.
The Spin Digital 8K HEVC real-time encoder produces similar quality to offline encoders at 20 times the encoding speed, and it results in a noticeable higher quality than real-time hardware encoders.
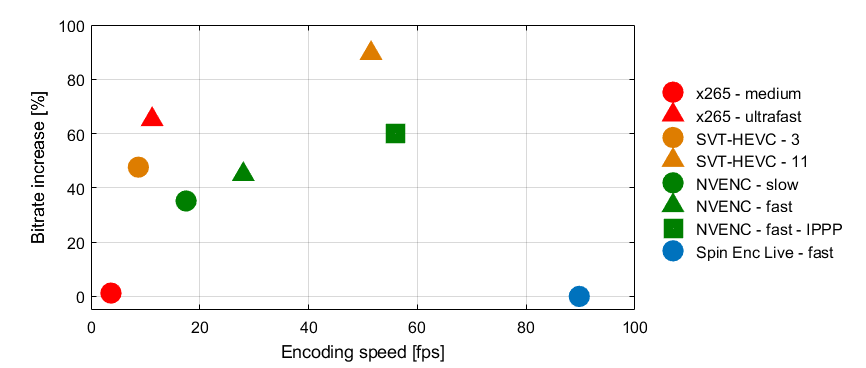
Bitrate increase of HEVC encoders referred to Spin Enc Live and encoding speed for 8K video
References
- Sullivan G. J., Ohm J. R., Han W. J., and Wiegand T., Overview of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Standard, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 1649-1668, Dec. 2012.
- Ohm J. R. et al., Comparison of the Coding Efficiency of Video Coding Standards – Including High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 1668-1683, Dec. 2012.